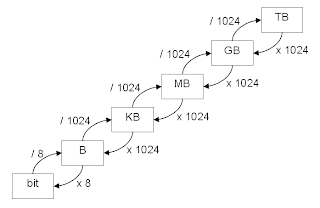
Units of information
In computing and telecommunications, a unit of information is the capacity of some standard data storage system or communication channel, used to measure the capacities of other systems and channels. In information theory, units of information are also used to measure the information contents or entropy of random variables.
The most common units are the bit, the capacity of a system which can exist in only two states, and the byte (or octet), which is equivalent to eight bits. Multiples of these units can be formed from these with the SI prefixes (power-of-ten prefixes) or the newer IEC binary prefixes (binary power prefixes). Information capacity is a dimensionless quantity.
Bit
The bit is a basic unit of information in computing and digital communications.
A bit can have only one of two values, and may therefore be physically implemented with a two-state device.
Byte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits.
Is the smallest addressable unit of memory in many computer architectures.
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information.
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Its recommended unit symbol is MB, but sometimes MByte is used.
Gigabyte
The gigabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Therefore, one gigabyte is 1000000000bytes. The unit symbol for the gigabyte is GB.
Terabyte
The terabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. And therefore one terabyte is one trillion (short scale) bytes. The unit symbol for the terabyte is TB.
1 TB = 1000000000000bytes = 1012bytes = 1000gigabytes.
Petabyte
The petabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. And therefore 1 petabyte is one quadrillion (short scale) bytes, or 1 billiard (long scale) bytes. The unit symbol for the petabyte is PB.
1 PB = 1000000000000000B = 1015bytes = 1000terabytes.
Exabyte
The exabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Therefore, one exabyte is one quintillion bytes (short scale). The symbol for the exabyte is EB.
1 EB = 10006bytes = 1018bytes = 1000000000000000000B =
Zettabyte
The zettabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. A zettabyte is one sextillion (one long scale trilliard) bytes.The unit symbol is ZB.
1ZB= 10007bytes = 1021bytes = 1000000000000000000000bytes = 1000exabytes
Yottabyte
The yottabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Therefore one yottabyte is one septillion (one long scale quadrillion) bytes. The unit symbol for the yottabyte is YB.
- 1YB= 10008bytes = 1024bytes = 1000000000000000000000000bytes
- = 1000zettabytes = 1trillionterabytes
Virus y anti-virus
Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, is any software used to disrupt computer or mobile operations, gather sensitive information, gain access to private computer systems, or display unwanted advertising.
Unite Convertion:
Unite Convertion:
Tech News:
Japan to launch self-navigating cargo ships 'by 2025'
Japanese shipping companies are working with shipbuilders to develop self-piloting cargo ships.
The "smart ships" will use artificial intelligence to plot the safest, shortest, most fuel-efficient routes, and could be in service by 2025.
The AI will also be used to predict malfunctions and other problems, which could help reduce the number of maritime incidents.
The companies plan to build about 250 self-navigating ships.
Sharing data
Developing the technology is expected to cost tens of billions of yen (hundreds of millions of dollars).
Shipping firms Mitsui OSK Lines and Nippon Yusen are working with shipbuilders including Japan Marine United to share both costs and expertise, according to the Nikkei Asian Review.
Nippon Yusen has already been working on technology to enable ships to use data to assess collision risks. It is also working with Norwegian maritime company DNV GL to collect and analyse data on vessel condition and performance.
Japan Marine has been developing a similar data analysis system with the aim of diagnosing breakdowns before they happen.
'Remote-controlled'
The first ships will retain a small crew to oversee certain operations, but there are plans to develop completely autonomous vessels in the future.
In 2016, Rolls-Royce announced plans to develop unmanned cargo ships, starting with remote-controlled vessels that could be operational as soon as 2020.
"This is happening. It's not if, it's when," Rolls-Royce vice president of marine innovation Oskar Levander said at the time.
"We will see a remote-controlled ship in commercial use by the end of the decade."
Navigation and basic operations will be automated, while a human "captain" based on shore will continue to look after "critical decision-making".